

Even though this program seems like its for skiddies it is however useful for someone who is still learning the tricks of the trade. I eventually moved onto forcing my wireless card into monitor mode myself mostly because of the mac addy problem you detail in your post. Attacking: Replay attacks, deauthentication, fake access points and others via packet injection. Airmon-ng helped me figure out the Aircrack suite. It focuses on different areas of WiFi security: Monitoring: Packet capture and export of data to text files for further processing by third party tools.
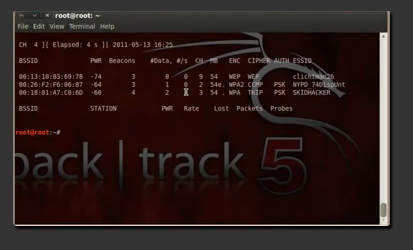
’00:00:00:00:00:00′ is the MAC address of the target client, NOT that of your own wireless card. Aircrack-ng is a complete suite of tools to assess WiFi network security. ’00:09:5B:D7:43:A8′ is the MAC address of my network, so you need to replace it with your own.Ĥ. This HOWTO was written for Aircrack-NG v0.9.1 & Aircrack-PTW v1.0.0 on Kubuntu Feisty Fawn 7.04 (32-bit).ģ.
Airmon ng mac driver#
You have successfully patched your wireless driver (see link above).Ģ.
Airmon ng mac install#
If you need help patching & compiling from source, feel free to post your problems here as well.īefore you proceed you need to compile your own drivers & install patches for packet re-injection. I recommend “Linksys WUSB54G V4.0” as it has a decent reception and reasonable performance. I have tested packet injection and decryption with:

Ralink chipset), so I won’t go into this. I assume that you have successfully patched the driver for your wireless adapter (e.g. Provided that you have collected a sufficient number of IVs (= Initialization Vectors) and depending on the length of the encryption key, determining the actual WEP key will take less than a minute on a common PC. Generally speaking there are 3 types of attacks:īy exploiting several security weaknesses of the WEP protocol Aircrack NG makes use of a statistical method to recover WEP keys. If you want the screenshots, you’l have to sign into the forums. I’ve copied the posters conents here, if you don’t want to deal with the link. It’s not advanced stuff, you can learn more about aircrack-ng in still interested. The article is geared for identifying wireless security holes and exploting them. Sure enough someone has, so take a look at the following link. However, before I made up a long winded post I decided to research it, see if someone else has done the work already.
Airmon ng mac how to#
?d?d?d?d?d?d?d?d : 8为数字破解 ,?d代表数字 hashcat -m 2500 -a 3 /tmp/output.So I wanted to show users how to sniff out their local wireless traffic, capture it and decrypt it. 删除hashcat.potfile中内容 find / -name "hashcat.potfile" cap2hccapx.bin /tmp/airportSniffxQnNSI.cap /tmp/output.hccapx MERCURY_1B44ĩ,hashcat破解密码 hashcat -m 2500 /tmp/output.hccapx /root/pass.txtĩ.1 hashcat 规则破解密码 INFO: All hashes found in potfile ! Use -show to display them. 2 - Install aircrack-ng: brew install aircrack-ng: 3 - Install the latest Xcode, with the Command Line Tools. $ aircrack-ng -w dic.txt wifiCap/handshake.capĥ,跑字典 aircrack-ng -w pass.txt /tmp/airportSniffxNVV5o.capĪircrack-ng -w pass.txt -b e4:f3:f5:93:1b:42 /tmp/airportSniffxNVV5o.cap $ mergecap -a -F pcap -w handshake.cap beacon.cap cap.cap $ sudo tcpdump "ether proto 0x888e and ether host e4:f3:f5:93:1b:42" -I -U -vvv -i en1 -w cap.cap $ sudo tcpdump "ether proto 0x888e and ether host e4:f3:f5:33:11:22" -I -U -vvv -i en1 -w cap.cap
Airmon ng mac plus#
Tcpdump: listening on en1, link-type IEEE802_11_RADIO (802.11 plus radiotap header ), capture size 262144 bytes $ sudo tcpdump "type mgt subtype beacon and ether src e4:f3:f5:33:11:22" -I -c 1 -i en1 -w beacon.cap WPA (1 handshake) 1成功抓到握手包 4.1,macos mojave airport sniff 报错 1,安装和更新aircrack-ng brew search aircrack-ngĪircrack-ng: stable 1.5.2 (bottled) 3,查看附近wifi sudo ln -s /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/amework/Versions/Current/Resources/airport /usr/local/bin/airportġ 破解Wi-Fi信道CHANNEL aircrack-ng /tmp/airportSniffxNVV5o.cap | grep 1B:42Īircrack-ng airportSniffxQnNSI.cap | grep "1 handshake"


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
